- Published on
Zero-Knowledge Proofs Privacy in Blockchain Applications
- Authors

- Name
- Adil ABBADI
Introduction
The blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about decentralized systems, enabling secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions. However, one of the major concerns in blockchain applications is privacy. Traditional public blockchain transactions are transparent, making it possible for anyone to trace the transaction history of a particular wallet address. This lack of privacy can be a significant issue for individuals and organizations that value confidentiality.
In this blog post, we'll delve into the concept of Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) and their role in ensuring privacy in blockchain applications while maintaining the integrity of transactions.
- What are Zero-Knowledge Proofs?
- Types of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
- Applications of Zero-Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain
- Challenges and Limitations of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
- Conclusion
- Ready to Explore Zero-Knowledge Proofs Further?
What are Zero-Knowledge Proofs?
Zero-Knowledge Proofs are cryptographic protocols that allow one party (the prover) to demonstrate the validity of a statement to another party (the verifier) without revealing any information about the statement itself. In other words, the verifier is convinced that the statement is true without learning anything about the underlying data.
The Zero-Knowledge Proof process involves three main properties:
- Completeness: If the statement is true, the prover can convince the verifier of its validity.
- Soundness: If the statement is false, no prover can convince the verifier of its validity, except with a small probability.
- Zero-Knowledge: The verifier learns nothing about the statement beyond its validity.
Types of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
There are two main types of Zero-Knowledge Proofs:
- Interactive Zero-Knowledge Proofs: The prover and verifier engage in multiple rounds of interaction to establish the validity of the statement.
- Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Proofs: The prover generates a proof that can be verified by the verifier without any interaction.
Applications of Zero-Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain
Zero-Knowledge Proofs have numerous applications in blockchain technology, including:
- Private Transactions: ZKPs enable users to make private transactions, ensuring that the transaction amount and parties involved remain confidential.
- Smart Contract Execution: ZKPs can be used to execute smart contracts while keeping the input data private, ensuring that sensitive information is not revealed.
- Identity Verification: ZKPs can be used to verify a user's identity without revealing any personal information, enabling secure and private authentication.
zk-SNARKs: A Popular Zero-Knowledge Proof System
One of the most popular Zero-Knowledge Proof systems is zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge). zk-SNARKs are a type of non-interactive Zero-Knowledge Proof that enables fast and efficient verification of complex statements.
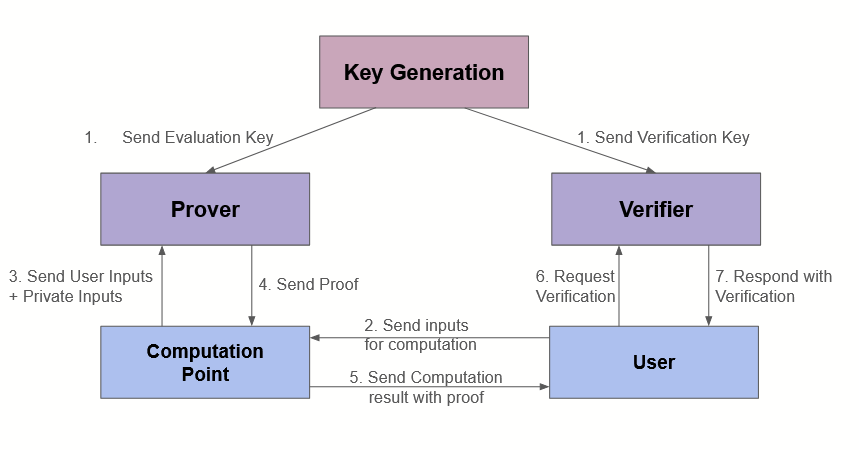
zk-SNARKs are widely used in blockchain applications, including Zcash and Ethereum, to enable private transactions and secure smart contract execution.
Challenges and Limitations of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
While Zero-Knowledge Proofs offer robust privacy guarantees, they also come with some challenges and limitations:
- Complexity: Zero-Knowledge Proofs can be computationally intensive and require significant resources.
- Scalability: ZKPs can be slow and may not be suitable for high-volume transactions.
- Security Risks: ZKPs are not immune to security risks, and vulnerabilities can be exploited if not implemented correctly.
Conclusion
Zero-Knowledge Proofs have the potential to revolutionize the way we think about privacy in blockchain applications. By enabling private transactions, secure smart contract execution, and identity verification, ZKPs can provide a robust solution for confidentiality in decentralized systems. While there are challenges and limitations to consider, the benefits of Zero-Knowledge Proofs make them an essential tool in the development of privacy-preserving blockchain applications.
Ready to Explore Zero-Knowledge Proofs Further?
Dive deeper into the world of Zero-Knowledge Proofs and discover the exciting possibilities they offer for privacy-preserving blockchain applications.
